Overview
- Always a balance between pro-aggregation and anti-aggregation forces
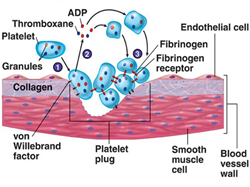
- Formation of a platelet plug occurs in four main stages
- Aggregation
- vasoconstriction results in decreased blood flow
- mediated by activated platelets which synthesize TxA2 by cyclooxygenase I enzymes
- COXI inhibited by aspirin which results in ↓ aggregation
- mediated by activated platelets which synthesize TxA2 by cyclooxygenase I enzymes
- PGI2 and NO released by endothelial cells are natural aggregation inhibitors by vasodilating vessels
- vasoconstriction results in decreased blood flow
- Swelling
- inter-platelet binding via fibrinogen cross links to GpIIb/IIIa receptors on platelet membrane
- GpIIb/IIIa inserted on membrane by binding of ADP to platelet ADP receptors
- once this step happens the bleeding stops and is the end of the “bleeding time” test
- although clot has formed, it is unstable and easily disrupted
- inter-platelet binding via fibrinogen cross links to GpIIb/IIIa receptors on platelet membrane
- Maturation
- fibrinogen is converted to fibrin with cross-linking to strengthen plug
- Ca2+ also strengthens platelet plug
- Aggregation



