Overview
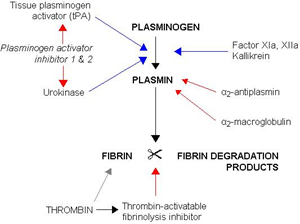
- Thrombolytics catalyze the formation of endogenous plasmin from plasminogen precursor
- plasmin is a serine protease that degrades clots (thrombi)
- Drugs
- tPA (alteplase)
- streptokinase
- urokinase
- APSAC (anistreplase)
- Mechanism
- catalyze conversion of plasminogen to plasmin
- cleaves fibrin clots
- cleaves thrombin
- clot-specificity
- tPA is clot-specific
- acts only on fibrin-bound plasminogen
- streptokinase is not clot specific
- depletes circulating plasminogen, factor V, factor VIII
- tPA is clot-specific
- ↑ PT, ↑ PTT, no change in platelet count
- catalyze conversion of plasminogen to plasmin
- Clinical use
- administer as early as possible following
- ischemic stroke (tPA)
- MI
- DVT
- pulmonary embolism
- administer as early as possible following
- Toxicity
- bleeding and intracerebral hemorrhage
- contraindicated in patients with history of bleeding, surgery, hypertension
- streptokinase may cause hypersensitivity
- derived from β-hemolytic streptococci
- bleeding and intracerebral hemorrhage
- Antagonist


