Thioamides
- Drugs
- propylthiouracil (PTU)
- methimazole
- Mechanism
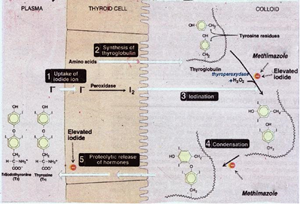
- inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis by blocking peroxidase-catalyzed reactions
- iodination of tyrosine residues of thyroglobulin
- coupling of DIT and MIT
- propylthiouracil ↓ peripheral conversion of T4 to T3
- inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis by blocking peroxidase-catalyzed reactions
- Clinical use
- HYPERthyroidism
- Toxicity
- skin rash
- aplastic anemia
- hepatotoxicity (PTU)
- PTU not used first line in non-pregnant adults and children for this reason
- Pregnancy
- methimazole crosses the placenta and enters breast milk (may be teratogenic)
Thyroid hormones
- Drugs
- levothyroxine
- synthetic T4 (thyroxine)
- triiodothyronine
- T3
- levothyroxine
- Mechanism
- replaces endogenous thyroid hormones
- Clinical use
- HYPOthyroidism
- myxedema
- Toxicity
- thyrotoxicosis
- heat intolerance
- tachycardia
- dyspnea
- ↑ appetite
- tremors
- arrhythmias
- thyrotoxicosis


