Overview
Snapshot
- A 40-year-old woman presents to her physician’s office for management of her newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis. She reports that she has not tried any long-term medication for this disease and seeks advice. She is counseled on the immunosuppressive effects of this class of medications and is tested for latent tuberculosis prior to starting therapy.
Introduction
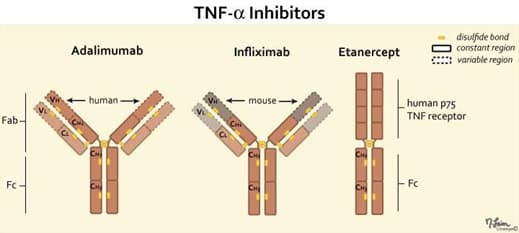
- Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors
- categories
- fusion proteins
- monoclonal antibodies
- categories
- Mechanism of action
- inhibits physiologic response to TNFα, an important component of inflammation
- Toxicity
- immunosuppression
- ↑ risk of infections
- ↑ risk of lymphomas
- immunosuppression
- must always test for tuberculosis prior to starting TNF-α inhibitors
Fusion Proteins
- Medications
- etanercept
- Mechanism of action
- fusion protein of the receptor for TNFα and immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 Fc
- produced by recombinant DNA
- acts as a decoy TNFα receptor
- fusion protein of the receptor for TNFα and immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 Fc
- Clinical use
- ankylosing spondylitis
- psoriasis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- Toxicity
- immunosuppression
- lupus-like syndrome
Monoclonal Antibodies


