Introduction
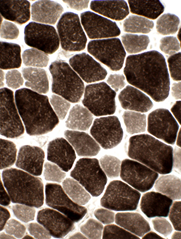
- Skeletal muscle consists of two types of muscle fibers
- type I
- type II
- type IIa
- type IIb
- Muscle fiber types vary across several characteristics
- resistance to fatigue
- color
- determined by an amount of myoglobin
- type of metabolism
- aerobic vs. anaerobic
- determined by relative amounts of mitochondria and glycogen
- Non-athletes will have approximately equal amounts of type I and type II muscle fibers
- Athletes will have different ratios of type I and type II muscle fibers depending on their predominant activities
Type I Muscle Fibers
- Also known as slow twitch muscle fibers
- Color
- red
- more myoglobin
- red
- Fatigue tolerance
- high
- able to maintain sustained contractions
- higher proportion in endurance runner’s muscles
- Type of metabolism
- Function
- postural control
- walking
- Mnemonic
- “One Slow Red Ox” = type I muscles are slow twitch, red, and use oxidative metabolism
Type II Muscle Fibers
- Also known as fast twitch muscle fibers
- Color
- white
- less myoglobin
- white
- Fatigue tolerance
- low
- best suited for short high-intensity contraction
- higher proportion in sprinter’s muscles
- Type of metabolism
- anaerobic
- contains less mitochondria
- contains more glycogen to carry out glycolytic metabolism
- anaerobic
- Subtypes
- type IIa
- “fast twitch oxidative”
- aerobic and anaerobic metabolism
- intermediate contraction strength
- type IIb
- “fast twitch glycolytic”
- anaerobic metabolism only
- highest contraction strength
- type IIa
- Function
- power activities
- sprinting
- powerlifting
- power activities


