Overview
Introduction
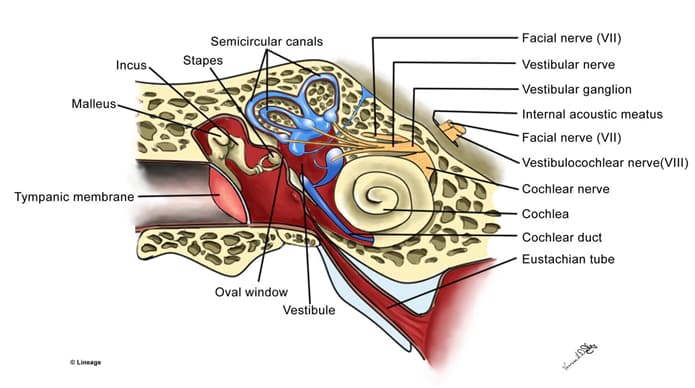
- Vestibular system
- angular acceleration of the head is detected by the semicircular canals
- linear acceleration of the head and head tilt is detected by maculae (which is contained within the utricle and saccule)
- maculae contain otolith (calcified crystals)
- otolith may be pulled with linear acceleration and activate hair cells which
- excites primary sensory neurons → vestibular ganglia → vestibular nerve
- vestibular nerve runs synapses to the vestibular nuclei which then relays to other structures within the central nervous system such as
- medial longitudinal fasciculus
- which mediates the vestibulo-ocular reflex
- spinal cord
- cerebellum (e.g., flocculonodular lobes and vermis)
- cerebral cortex via the thalamic ventral posterior nucleus
- medial longitudinal fasciculus
- vestibular nerve runs synapses to the vestibular nuclei which then relays to other structures within the central nervous system such as
- excites primary sensory neurons → vestibular ganglia → vestibular nerve
- otolith may be pulled with linear acceleration and activate hair cells which
- maculae contain otolith (calcified crystals)
- Clinical correlate
- caloric testing
- a test that stimulates the vestibulo-ocular reflex via
- warm or cold water infusion into the ear
- normal findings
- warm water
- nystagmus with the fast phase towards the side of infused water
- cold water
- nystagmus with the fast phases towards the opposite side of infused water
- mnemonic
- COWS (Cold Opposite, Warm Same)
- warm water
- a test that stimulates the vestibulo-ocular reflex via
- nystagmus
- describes rhythmic movements of the eye which can result from
- an asymmetric vestibular inputs
- describes rhythmic movements of the eye which can result from
- vertigo
- caloric testing


