Overview
- Recombination
- exchange of genes between 2 chromosomes
- crossing over occurs in homologous regions
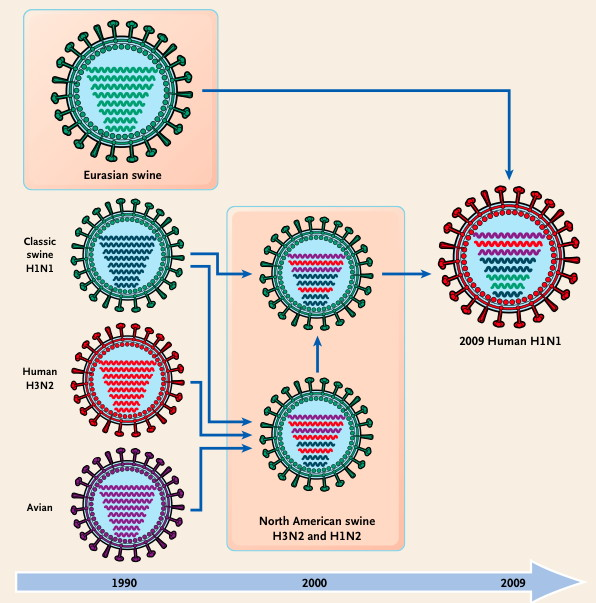
- Reassortment
- viruses with segmented genomes exchange segments
- analagous to high-frequency recombination
- results in influenza pandemics
- Complementation
- 2 viruses infect a cell, but one is mutated and has a non-functional protein
- the nonmutated virus helps the mutant by making protein for both viruses
- Phenotypic mixing
- 2 viruses infect a cell
- virus A has its own genetic material, but the surface proteins of virus B
- progeny viruses contain coat components and genetic material from virus A
- this is because they only had the genetic material from virus A
- genetic material is not altered
- pseudovirion formation
- when a virus’s coat is entirely from another virus
- nucleic acid and coat are completely mismatched


