Overview
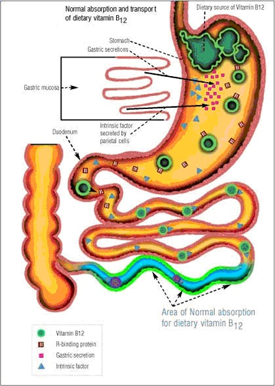
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
- gastrectomy
- IF deficiency as a consequence of loss of parietal cells
- IF deficiency → vitamin B12 deficiency
- may cause pernicious anemia
- treatment is vitamin B12 administered by injection
- may cause pernicious anemia
- IF deficiency → vitamin B12 deficiency
- IF deficiency as a consequence of loss of parietal cells
- gastrectomy
- Iron (Fe)
- absorption across apical membrane of intestinal epithelial cells occurs as free iron (Fe2+)
- in intestinal epithelial cells, free iron (Fe2+) binds apoferritin
- iron-ferritin complex is transported across basolateral membrane into bloodstream
- in bloodstream, iron binds transferrin and is transported from intestine to storage sites in liver
- iron-ferritin complex is transported across basolateral membrane into bloodstream
- in intestinal epithelial cells, free iron (Fe2+) binds apoferritin
- absorption across apical membrane of intestinal epithelial cells may also occur as heme iron
- in intestinal epithelial cells, heme iron (iron bound to hemoglobin) is digested by lysosomal enzymes
- releases free iron (Fe2+), which binds apoferritin
- in intestinal epithelial cells, heme iron (iron bound to hemoglobin) is digested by lysosomal enzymes
- absorption across apical membrane of intestinal epithelial cells occurs as free iron (Fe2+)
- Folic acid (folate)
- absorption occurs in the jejunum
- small reserve pool stored in the liver



