napshot
- A 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with prolonged bleeding after a dental procedure early that day. She has gone through several gauze packing with no success. Her past medical history includes heavy and prolonged menses. As a child, she had several episodes of unexplained nosebleeds. Labs show normal PT, PTT, and platelet count.
Introduction
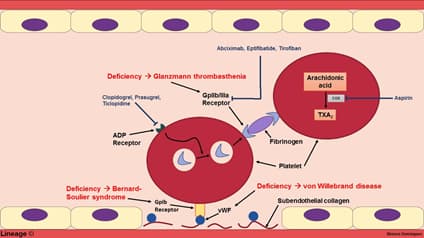
- Inherited mixed platelet and coagulation disorder from deficiency in von Willebrand factor (vWF)
- Genetics
- autosomal dominant
- Epidemiology
- most common inherited bleeding disorder
- more likely in Caucasians
- Pathogenesis
- affects coagulation – vWF carries and protects factor VIII
- produced by endothelial cells and megakaryocytes
- affects platelets – vWF is important in platelet adherence to endothelial lining
- affects coagulation – vWF carries and protects factor VIII
- platelet aggregation is normal (mediated by fibrinogen)
Presentation
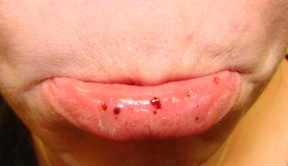
- Symptoms
- mucocutaneous bleeding
- epistaxis
- gingival bleeding
- petechiae
- easy bruising
- menorrhagia
- mucocutaneous bleeding
- increased bleeding after aspirin use
Evaluation
- Normal or ↑ PTT (like hemophilia)
- Normal PT
- ↑ bleeding time (unlike hemophilia)
- CBC
- normal platelet count and appearance
- may have anemia
- Diagnosis by ristocetin cofactor assay
- tests ability of platelets to bind to ristocetin (artificial endothelial surface)
- ↓ platelet agglutination
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- DDAVP (desmopressin acetate)
- releases vWF stored in endothelial cells
- Factor VIII replacement if refractory to DDAVP
- contains vWF
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- most are mild or moderate in severity
- Prevention
- avoid aspirin
- Complications
- excessive bleeding


